Highlights
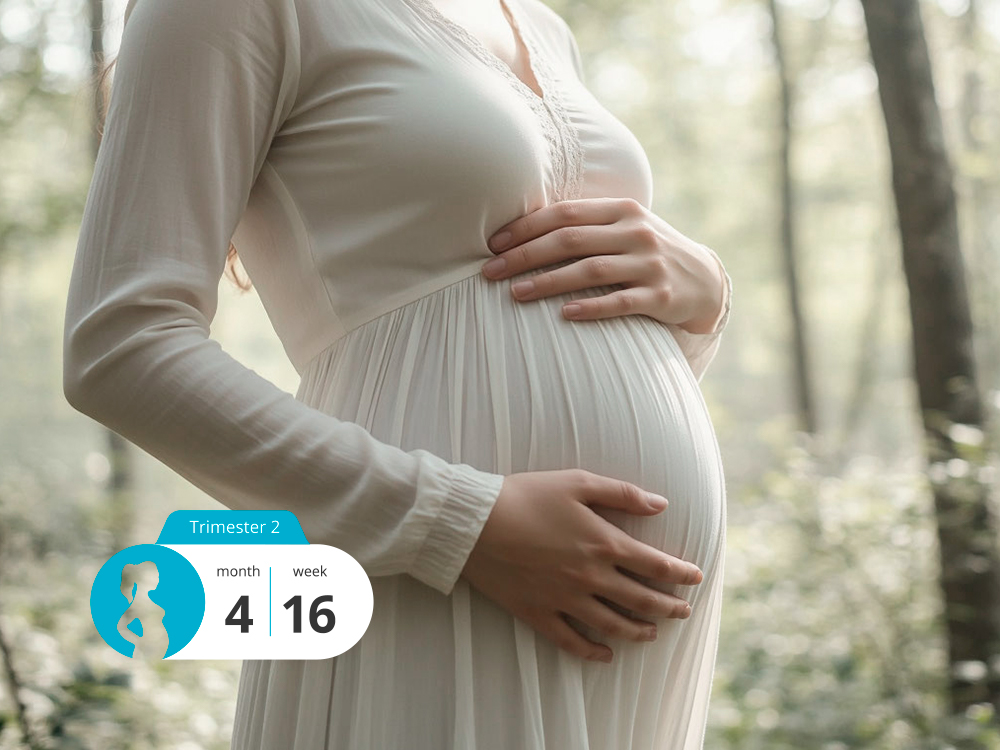
- Marks the end of the 4th month of pregnancy.
- Early discomforts such as nausea, abdominal tension, and mood swings usually subside.
- The fetus measures about 108–116 mm and weighs around 80 g, similar in size to an avocado.
- Noticeable weight gain and appetite increase are common at this stage.
- The uterus expands, causing visible changes in the abdomen.
- First fetal movements may be felt.
- Screening tests such as the triple test and, in certain cases, amniocentesis may be offered.
In This Article
- Maternal Well-being and Physical Changes
- Digestive and Respiratory Adjustments
- Fetal Development at 16 Weeks
- End of the Fourth Month of Pregnancy
- Sexual Activity During Pregnancy
- Ultrasound at 16 Weeks
- Laboratory Tests and Screenings
- Possible Complications and Warning Signs
- Body Pains and Discomforts
- Vaginal Discharge and Bleeding
- Fever, Cold, and Infections
- Lifestyle and Self-Care Recommendations
- Nutrition Guidelines
- Tools and Assistance
Maternal Well-being and Physical Changes
By the 16th week, many individuals experience a more stable and comfortable state compared to the first trimester. Typical sensations include:
- A healthy increase in appetite after the decline of early pregnancy nausea.
- Noticeable weight gain, averaging up to 3 kg since conception.
- A more visible abdominal bump, often difficult to conceal.
- Frequent urination, as the growing uterus presses on the bladder.
- Occasional shortness of breath, caused by uterine pressure on the diaphragm.
- A temporary pregnancy-related nasal congestion (physiological rhinitis).
- The first gentle fetal movements, often described as light flutters.
Digestive difficulties such as constipation may also occur, highlighting the importance of a fiber-rich diet.
Fetal Development at 16 Weeks
At this stage, the fetus continues rapid growth and development:
- Size and weight: ~108–116 mm in length, ~80 g in weight.
- Skeletal system: Bones strengthen; muscles develop.
- Movements: Limbs move more actively; facial muscles allow frowning, yawning, and opening/closing of the mouth.
- Neck control: Improved strength allows head movement side to side.
- Organs in function: The liver, kidneys, bladder, stomach, intestines, and gallbladder are active.
- Cardiovascular system: Heart rate averages 150 bpm, pumping ~25 liters of blood per day.
- External features: Mouth, ears, eyes, eyelashes, and eyebrows are well-formed.
The fetus requires adequate protein, calcium, iron, and vitamins for continued development.
End of the Fourth Month
By obstetric calculation, week 16 corresponds to the end of the 4th month of pregnancy. In calendar months, this is approximately the third week of the fourth month.
Sexual Activity During Pregnancy
Sexual activity is generally safe at 16 weeks unless contraindicated due to conditions such as placenta previa, risk of miscarriage, or multiple pregnancy. Healthcare providers may give specific recommendations based on individual health.
Ultrasound at 16 Weeks
A routine ultrasound is not always scheduled at this stage, but it may be recommended if there are symptoms or abnormal test results.
Ultrasound can show:
- Fetal size (~117 mm, 80 g).
- Active movements and reactions to stimuli.
- Facial and skeletal structures.
- In some cases, the baby’s sex, though accuracy is not guaranteed.
Laboratory Tests and Screenings
- Triple test: Evaluates hCG, estriol, and alpha-fetoprotein to screen for developmental abnormalities.
- Amniocentesis: Conducted only when medically indicated.
- Doppler ultrasound: May be recommended if maternal or fetal health concerns arise.
These examinations help in early detection of possible complications.
Possible Complications and Warning Signs
Missed Miscarriage
Weeks 16–18 are considered critical for possible fetal loss. Causes may include:
- Maternal infections.
- Rh incompatibility.
- Low progesterone levels.
- Genetic abnormalities.
- Lifestyle and environmental factors.
Warning signs include abdominal pain, brown discharge, fever, and weakness. Diagnosis requires ultrasound and blood tests for hCG.
Body Pains and Spasms
Mild discomfort is common due to uterine growth, but persistent or severe pain should be evaluated. Possible sensations include:
- Rib and lower back pain.
- Abdominal cramps from stretching muscles.
- Headaches from circulatory changes.
- Leg pain and swelling.
Vaginal Discharge and Bleeding
- Normal: Mild increase, clear or whitish.
- Watery: May suggest amniotic fluid leakage.
- Thick/curd-like: Could indicate yeast infection.
- Yellowish with odor: Possible infection.
- Bloody: Requires urgent medical care.
Fever, Cold, and Infections
A temperature up to 37°C may be normal. Higher readings with cough or congestion may indicate infection.
- Safe approaches: Adequate hydration, rest, gargling, saline rinses.
- Medication: Paracetamol may be used under supervision.
- Avoid: Aspirin, saunas, and mustard plasters.
Seek medical attention if temperature rises above 37.5–38°C.
Lifestyle and Self-Care Recommendations
- Choose comfortable clothing and footwear made from natural fabrics.
- Take daily walks to improve oxygen supply and well-being.
- Eat balanced meals rich in calcium, iron, fiber, and vitamins.
- Practice gentle self-massage with safe oils to help prevent stretch marks.
- Sleep on the side, preferably the left, to reduce pressure on the uterus.
Nutrition Guidelines
- Eat small, frequent meals throughout the day.
- Prioritize whole grains, fresh fruits and vegetables, lean meat, fish, and dairy.
- Drink at least 2 liters of water daily.
- Avoid alcohol, caffeine, unwashed produce, and raw/undercooked foods.
Balanced nutrition ensures steady fetal growth without excessive maternal weight gain.
Tools and Assistance
- Nutritional planners and meal trackers for balanced diet management.
- Pregnancy apps to track development and symptoms.
- Prenatal yoga or fitness classes for safe activity.
- Online and local support groups for emotional well-being.
- Home health tools (blood pressure monitor, weight scale).











Please log in to leave a comment.