Highlights
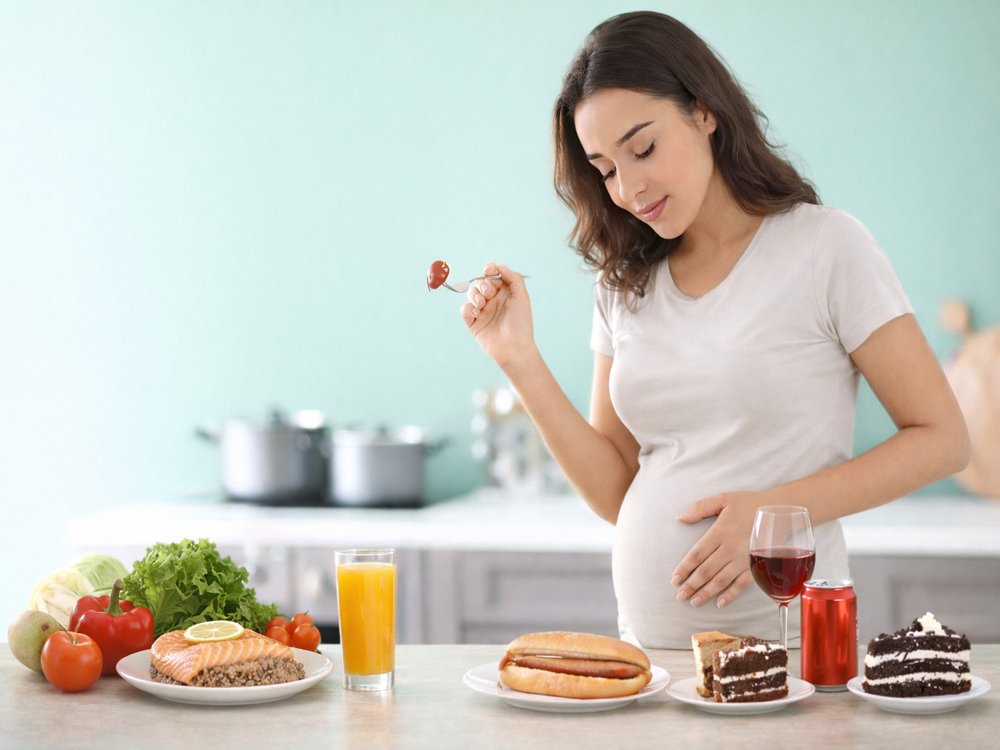
Maintaining a healthy diet during pregnancy is crucial for the well-being of both you and your baby.
Some foods may contain harmful bacteria, toxins, or substances that can negatively affect fetal development.
Key dietary guidelines for pregnancy:
- Eat a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, dairy, and whole grains.
- Avoid raw or undercooked meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products made from unpasteurized milk.
- Limit caffeine intake and eliminate alcohol consumption entirely.
- Be cautious with leftovers—store them properly and consume them within 24 hours.
- Follow safe food handling and hygiene practices.
In This Article
- Foods to Avoid During Pregnancy
- The Risks of Certain Foods
- How to Make Sure the Food You Eat Is Safe
- Caffeine and Alcohol Consumption During Pregnancy
- Eating Leftovers and Allergenic Foods
- Tools And Assistance
Foods to Avoid During Pregnancy
During pregnancy, the immune system becomes weaker, making you more susceptible to infections that may not affect non-pregnant individuals. Some foods pose a higher risk of contamination with bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Others contain substances that, in excessive amounts, can harm fetal development.
Foods to avoid:
- Soft cheeses (brie, camembert, blue cheese, ricotta, feta) unless cooked thoroughly
- Unpasteurized milk and dairy products
- Undercooked or raw meat, poultry, and fish
- Raw or lightly cooked eggs (e.g., homemade mayonnaise, aioli, hollandaise sauce)
- Processed and deli meats (unless heated to steaming hot)
- Cold-smoked seafood and raw fish (sushi, sashimi, smoked salmon)
- Raw sprouts and unwashed vegetables
- Liver and liver-based products (due to high vitamin A content)
- Alcohol
Foods to limit:
- Caffeinated drinks (coffee, tea, energy drinks, cola)
- Certain fish species (shark, swordfish, marlin, orange roughy, catfish) due to mercury levels
- Highly processed foods (fast food, chips, processed snacks)
The Risks of Certain Foods
Each of these foods carries specific risks. Some can cause food poisoning, while others contain substances that may affect fetal development.
Listeriosis
Listeriosis is caused by the bacteria Listeria monocytogenes. While rare, it is particularly dangerous for pregnant women and can lead to miscarriage, stillbirth, or premature labor.
High-risk foods for listeria contamination:
- Soft cheeses and unpasteurized dairy products
- Cold-smoked seafood and raw fish
- Deli meats, pâté, and cold chicken
- Pre-packaged or pre-cut fruit and salads
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic infection that, if contracted during pregnancy, can cause brain damage or vision problems in the baby.
High-risk foods for toxoplasmosis:
- Undercooked or raw meat
- Unwashed fruits and vegetables
- Contaminated water sources
Salmonella
Salmonella can cause severe food poisoning and, in rare cases, miscarriage.
High-risk foods for salmonella contamination:
- Raw or undercooked eggs
- Homemade sauces or desserts made with raw eggs
- Undercooked poultry
- Raw sprouts
Mercury Exposure
Mercury, found in high amounts in certain fish, can interfere with brain and nervous system development in the fetus.
Fish with high mercury levels to limit:
- Shark
- Marlin
- Swordfish
- Orange roughy
- Catfish
Vitamin A Overdose
While vitamin A is essential for fetal development, excessive intake (particularly from animal sources like liver) can cause birth defects.
Limit consumption of:
- Liver and liver-based products (no more than 50 grams per week)
How to Make Sure the Food You Eat Is Safe
Following food safety guidelines can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses during pregnancy.
General food safety tips:
- Wash hands thoroughly before handling food and after touching raw meat.
- Cook meat, poultry, and seafood to safe internal temperatures.
- Store perishable foods in the refrigerator and consume them before their expiration date.
- Wash all fruits, vegetables, and herbs under running water before eating.
- Avoid sharing utensils, plates, or drinks with others to minimize the risk of contamination.
Dairy Products
- Consume only pasteurized milk and dairy products.
- Avoid soft cheeses unless cooked to 75°C and eaten immediately.
- Hard cheeses like cheddar and parmesan are safe to eat.
Eggs
- Always cook eggs thoroughly until both the white and yolk are solid.
- Avoid homemade sauces, desserts, or dishes containing raw eggs.
Meat and Poultry
- Cook all meat and poultry until there is no pink color left.
- Avoid cold deli meats and pâté unless reheated to at least 75°C.
- Use separate chopping boards for raw meat and vegetables.
Fish and Seafood
- Consume only fully cooked fish and seafood.
- Avoid sushi, sashimi, and cold-smoked fish.
- Follow safe guidelines for mercury consumption in fish.
Fruits and Vegetables
- Wash thoroughly under running water to remove bacteria and pesticides.
- Avoid pre-cut fruit and salad bars, as they have a higher risk of contamination.
- Do not consume raw sprouts due to potential bacterial growth.
Water Safety
- If drinking water quality is uncertain, use bottled water or boil water before consumption.
- Avoid iodine-based water treatment methods, as excess iodine can affect fetal thyroid function.
Caffeine and Alcohol Consumption During Pregnancy
There is no known safe level of alcohol consumption during pregnancy. Even small amounts may affect fetal development and increase the risk of:
- Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD)
- Low birth weight
- Premature birth
- Learning disabilities
The safest choice is to completely avoid alcohol during pregnancy.
Caffeine Consumption:
Moderate caffeine intake is generally considered safe, but excessive amounts may increase the risk of miscarriage, preterm birth, and low birth weight.
Recommended daily caffeine limit: 200 mg per day
Caffeine content in common beverages:
- Instant coffee (1 tsp) – 80 mg
- Espresso (1 shot) – 145 mg
- Black tea (1 cup) – 50 mg
- Cola (375 ml can) – 36 mg
- Energy drink (250 ml can) – 80 mg
- Milk chocolate (100 g bar) – 20 mg
To reduce caffeine intake, opt for decaffeinated coffee, herbal tea, or water. Energy drinks are not recommended due to high caffeine levels and added stimulants.
Eating Leftovers and Allergenic Foods
Eating Leftovers:
Leftovers can pose a risk of Listeria contamination if not stored and reheated properly.
Safety tips for eating leftovers:
- Refrigerate within two hours of cooking.
- Store in a covered container and consume within 24 hours.
- Reheat to at least 60°C before eating.
Eating Allergenic Foods:
There is no evidence that avoiding allergenic foods during pregnancy prevents allergies in the baby. Unless you have a personal allergy, it is safe to eat:
- Fish and shellfish
- Peanuts and peanut butter
- Eggs
- Dairy
Tools And Assistance
If you’re finding it challenging to follow dietary recommendations during pregnancy, there are a variety of tools and support options available to help you make healthy choices:
- Consultations with Health Professionals: Talk to your obstetrician, general practitioner, or a registered dietitian. They can help you create a personalized meal plan based on your specific needs, preferences, and any health considerations.
- Food Diary: Keeping a food journal can help you monitor your daily intake and identify any nutritional gaps. It can also be a useful tool when discussing your diet with a healthcare provider.
- Meal Planning: Planning your meals for the week in advance helps avoid impulsive food choices and encourages healthier eating habits.
- Pregnancy and Nutrition Tracking Apps: Mobile apps can remind you to eat regular meals, track your vitamin and nutrient intake, log water consumption, and offer pregnancy-friendly recipes.
- Mental Health Support: Taking care of your emotional well-being is just as important as physical health. If you feel anxious about food, body image, or experience external pressures, talking to a mental health professional can be beneficial.
- Partner and Family Support: Share your nutritional goals with your partner and family. Getting them involved in grocery shopping, cooking, and mealtime routines can help you stay on track and make healthy eating a shared experience.











Please log in to leave a comment.